Low Carbon Energy - Biogas from AD Plants; Waste-to-Energy
Anaerobic Digestion - Low Carbon Climate Solution
Instead of waste simply ending up in landfills, or being incinerated, waste can be turned into renewable energy by use of anaerobic digestion (AD). Anaerobic digestion is a process of producing energy from waste and other organic materials typically used in biomass/ biofuel production.
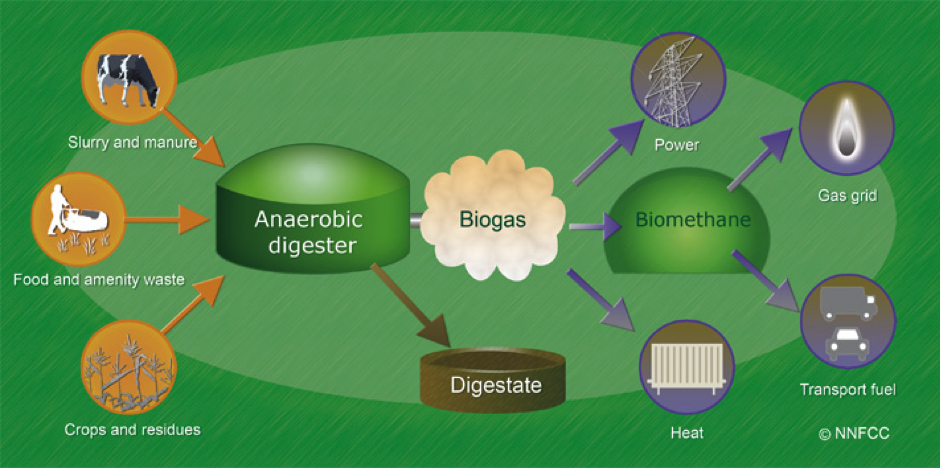
AD can be applied to municipal, commercial, and industrial waste, in addition to agriculture. There are a number of applications, besides farms, for AD plants; such as use for businesses and municipalities. AD is used for many purposes, from the production of renewable energy for use on municipal grids, to heating for farms, homes, and buildings, to the production of biofuel for use in transportation.
Examples of feedstocks for AD are agricultural waste (such as livestock manure, and/ or other organic waste from agricultural processes), wastewater, municipal waste streams, energy crops and/ or other crops, food processing waste, biodegradable organic material, sewage, and other waste streams. The use of AD can make farms and wastewater treatment facilities energy-neutral or even energy-positive, translating to huge cost savings for municipalities.
Through the use of AD, farms, homes, and small businesses can be powered by waste normally simply disposed of (animal waste, food waste, crop/ agricultural waste, household waste, and other waste streams.).
How is the energy produced through AD used?
The renewable energy generated through AD can be used for - the municipal power and gas grid, just the farm(s) with the AD units (as in on-site anaerobic digesters on farms), energy to heat and cool homes, or even fuel for the transportation sector.
AD can supply biomethane (after a conversion process known as methanization) to municipalities, residences, and buildings to provide energy and heat (as discussed in the 'anaerobic digestion process and applications' section below. [Note: AD can produce fuel only after being converted into a usable form for transportation fuel, as discussed below.]
Organic waste finds a constructive purpose in an AD biogas plant, as the waste is transformed into renewable energy.
Other than energy, what else is produced through anaerobic digestion?
AD also produces numerous beneficial by-products (digestate by-products) for farms. Examples are animal bedding, and low-cost fertilizer or enhanced organic fertilizer (from digestate that has a large number of nutrients and can enhance soil).
The molecules of the organic waste used in an anaerobic digester are broken down by the micro-organisms in the AD plant into a useful form, like glucose. The "digested" raw material is used to create biogas. The remaining material can then be harvested as nitrogen and phosphorus-rich digestate, which can be used as fertilizer. The remaining material can also be used in animal bedding.
Biogas can be processed and purified for the first step in the process of creating transportation fuel from AD (the gas can also be upgraded with hydrogen for use as pipeline-quality synthetic natural biogas for the grid). Biogas can then be converted into biomethane.
Biomethane can then be further processed into liquefied natural gas (LNG), or compressed natural gas (CNG). These types of gas fuels, technically bio-natural gas when sourced from the AD process, are used for vehicles, tractors, or other farm equipment (or even for transportation fuels for public buses, as discussed below in the section about Oslo's bio-fueled bus fleet).
The use of these fuels requires vehicles to be modified to run on LNG or CNG. (Technically, both of these fuels, when produced through AD, are termed bio-LNG and bio-CNG).
Anaerobic digestion process and applications

Anaerobic digestion uses micro-organisms (enzymes, bacteria etc...) in an anaerobic digester. AD can be used in the form of a municipal anaerobic digestion power plant. However, AD is more commonly used in on-site anaerobic power plants, as in an anaerobic digester on a large farm. Anaerobic digesters break down organic material and create biogas.
In addition, the AD process can be the first step in creating bio-LNG and bio-CNG. Biogas can also be converted into syngas (SNG), after being upgraded with hydrogen. (Synthetic natural gas created through AD is technically termed bio-SNG).
The anaerobic process also occurs naturally in landfills. The process of using methane produced naturally in landfills (for municipal energy grids) is one example of the use of biogas as renewable energy. Clean, renewable energy, in the form of biomethane, is created through the process of methanation in a wide variety of AD plants, biogas plants, and methanation plants.
AD plants are found on farms, in landfills, and in municipalities throughout the world. Because an AD plant generates biogas (and/ or biomethane) that is often burned on-site to generate heat, energy, or both - the process of anaerobic digestion easily can be integrated into combined heat and power (CHP) plants as well.
Waste-to-energy in conjunction with AD
In addition to AD, waste-to-energy (W2E) is generated in landfills, using landfill garbage and landfill gases (methane and CO2). The use of AD in a biomass plant, and waste-to-energy, are cost-effective ways to produce renewable energy. Waste-to-energy also leads to less landfill waste. It is a constructive way for farms, businesses, and municipalities, to dispose of waste. Waste-to-energy creates renewable energy for municipal grids, energy for farms, heat for homes, and even transportation fuel.
When biogas is used for transportation, as bio-LNG or bio-CNG - both fuels can be used in place of diesel, given modifications to the vehicles in question. With the use of these fuel types, there are significant greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) reductions.
A selection of buses in Oslo, Norway are run on bio-CNG produced from sewage treatment and organic waste. These buses see a dramatic (around 70%) reduction in GHGs compared to fossil fuel-burning vehicles. Food waste and other waste processed through AD also bring the benefit of reducing GHGs substantially by reducing landfill waste.
Also, when AD is used for on-site electrical generation, and energy generation for a municipality, farm, or wastewater facility, GHGs overall are greatly reduced. The energy and fuel produced by AD have a very low overall carbon footprint.
/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-expressandstar-mna.s3.amazonaws.com/public/TE4PLA7RXJDPFDW23MP27YFFYY)
The AD plant at Cannock, Staffordshire, England (called the Poplars AD plant), is an example of a successful, large-scale AD plant. The £24 million project treats commercial and industrial waste streams to create, through methanation, around 6MW of renewable energy for the national grid. The Poplars plant also produces SNG and other products through the AD process.
The Poplars plant shows that a large-scale anaerobic digestion project is viable. AD has been successful in many commercial operations as well; from Europe to Indiana, to China and India, and in dozens of countries throughout the world.
Another large-scale anaerobic digestion facility with success in a commercial application is in Orlando, Florida, from food (and other) waste sourced primarily from the Walt Disney World Resort. The AD plant near Disney World is fed with waste from the amusement park's operations to produce renewable energy.
The California company Clean World developed a biodigester for Sacramento. This Sacramento biogas plant transforms 100 tons of food waste per day into natural gas, electricity, and fertilizer.
Please see:
Renewable Energy: Biomass and Biofuel
Please also see:
Gasification - Syngas From Fossil Fuels and Environmentally Friendly Versions